Process Maps, Flow Charts and Case Studies
The experience of the adult at risk
The procedures to deliver this
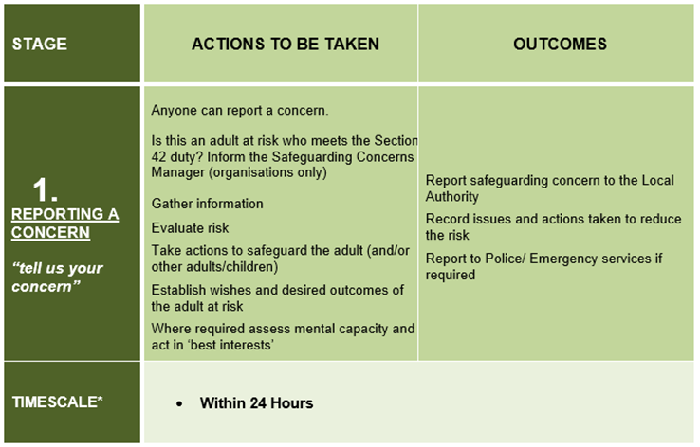
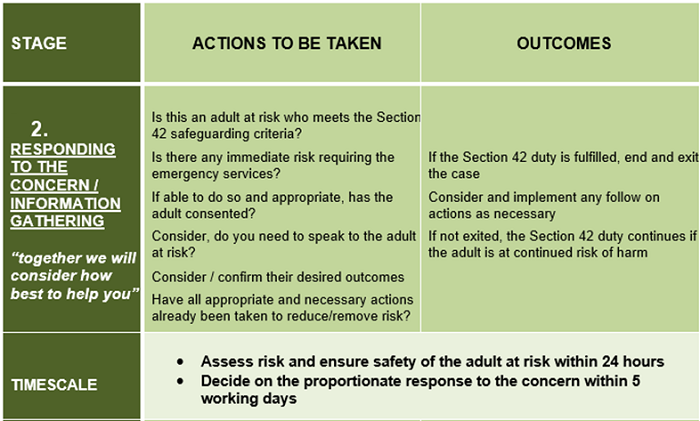
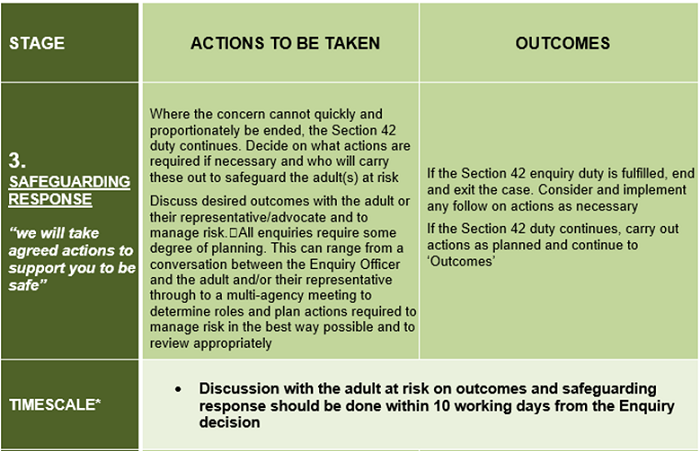
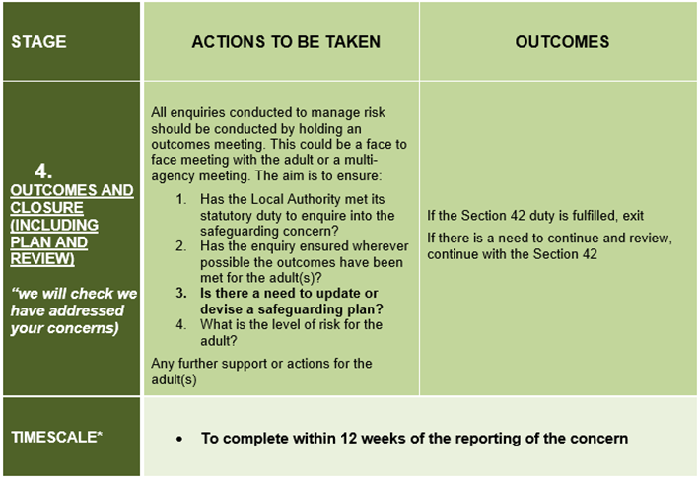
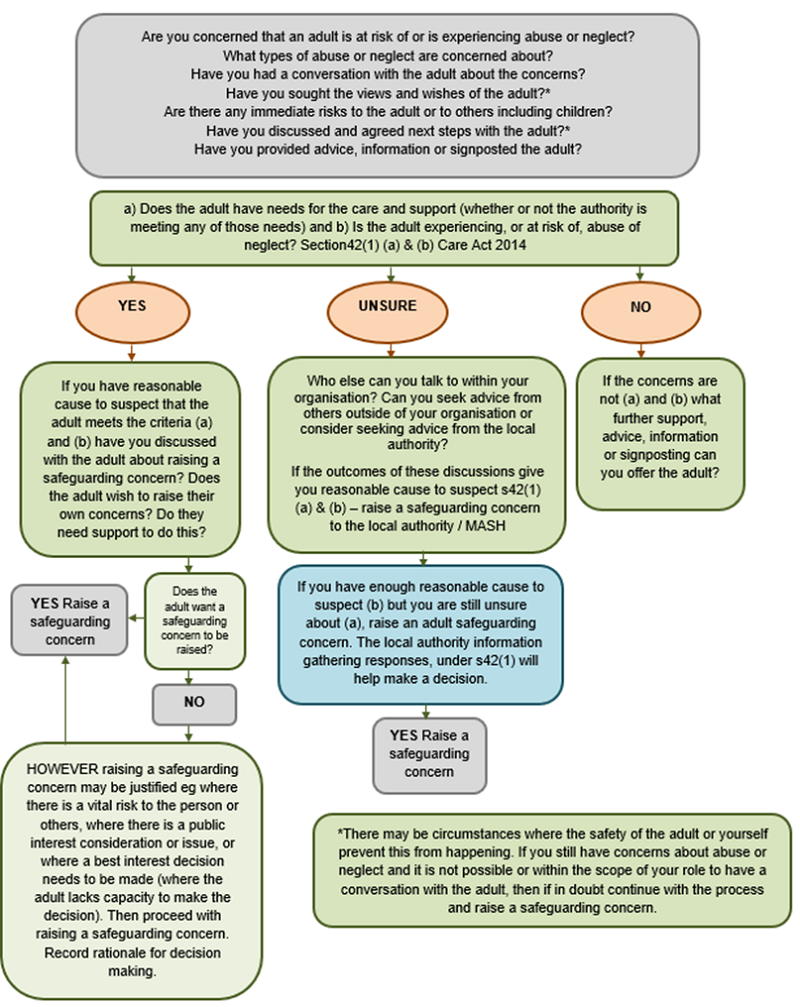
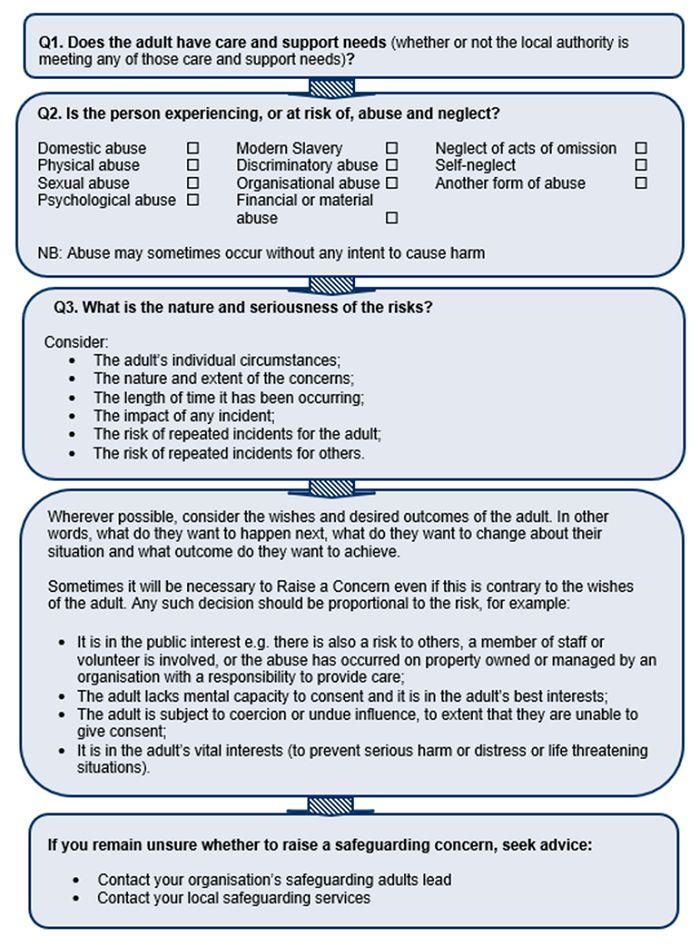
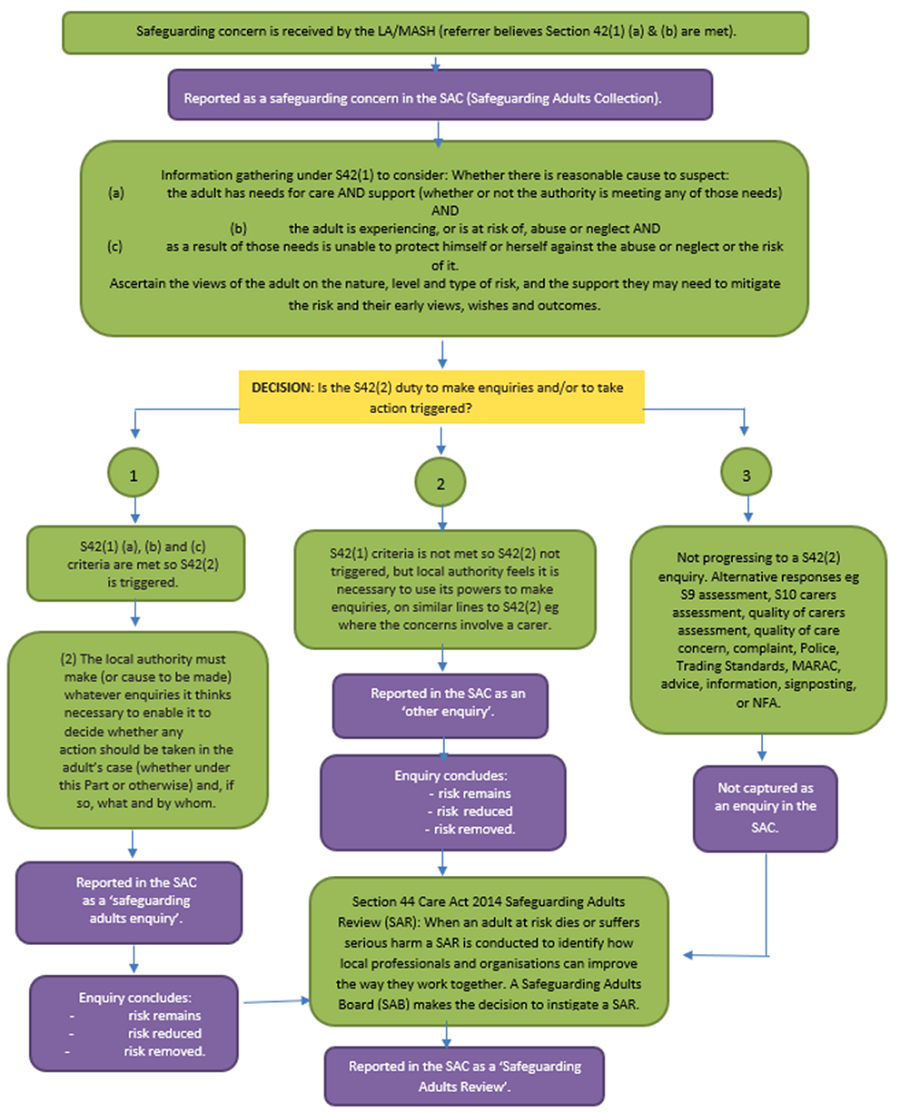
The time taken to respond to a safeguarding concern(s) will depend on a range of factors, including the wishes and needs of the adult at risk, as well as the nature, seriousness and complexity of the concern(s).
Note: The timescales described within these procedures are not intended as performance indicators, however provide useful targets for practice that are achievable in many cases. The timescales need to reflect:
- All other investigations such as NHS Serious Incidents (SI);
- The investigation that takes priority – this needs to be agreed on a case by case basis.
The following case studies are all taken from the Care Act Statutory Guidance.
Two brothers with mild learning disabilities lived in their family home, where they had remained following the death of their parents some time previously. Large amounts of rubbish had accumulated both in the garden and inside the house, with cleanliness and self-neglect also an issue. They had been targeted by fraudsters, resulting in criminal investigation and conviction of those responsible, but the brothers had refused subsequent services from adult social care and their case had been closed.
They had, however, had a good relationship with their social worker, and as concerns about their health and wellbeing continued it was decided that the social worker would maintain contact, calling in every couple of weeks to see how they were, and offer any help needed, on their terms. After almost a year, through the gradual building of trust and understanding, the brothers asked to be considered for supported housing; with the social worker's help they improved the state of their house enough to sell it, and moved to a living environment in which practical support could be provided.
This case study highlights the need for local authorities not to underestimate the potential impact of financial abuse:
Mrs B is an 88 year old woman with dementia who was admitted to a care home from hospital following a fall. Mrs B appointed her only daughter G, to act for her under a Lasting Power of Attorney in relation to her property and financial affairs.
Mrs B's former home was sold and she became liable to pay the full fees of her care home. Mrs B's daughter failed to pay the fees and arrears built up, until the home made a referral to the local authority, which in turn alerted the Office of the Public Guardian (OPG).
The OPG carried out an investigation and discovered that G was not providing her mother with any money for clothing or toiletries, which were being provided by the home from its own stocks. A visit and discussion with Mrs B revealed that she was unable to participate in any activities or outings arranged by the home, which she dearly wished to do. Her room was bare of any personal effects and she had limited stocks of underwear and nightwear.
The Police were alerted and interviewed G, who admitted using the proceeds of the mother's house for her own benefit. The OPG applied to the Court of Protection for suspension of the power of attorney and the appointment of a deputy, who was able to seek recovery of funds and ensure Mrs B's needs were met.
This case study demonstrates how anyone can become aware of information suggesting that abuse and neglect is occurring:
Mr A is in his 40s, and lives in a housing association flat, with little family contact. His mental health is relatively stable, following a previous period of hospitalisation and he has visits from a mental health support worker.
He rarely goes out, but he allows people into his accommodation because of his loneliness. The police were alerted by Mr A's neighbours to several domestic disturbances. His accommodation had been targeted by a number of local people and he had become subjected to verbal, financial and physical abuse. Although Mr A initially insisted they were his friends, he did indicate he was frightened; he attended a case conference with representatives from adult social care, mental health services and the police, from which emerged a plan to strengthen his own self-protective ability as well as to deal with the present abuse.
Mr A has made different arrangements for managing his money so that he does not accumulate large sums at home. A community-based visiting service has been engaged to keep him company through visits to his home, and with time his support worker aims to help get involved in social activities that will bring more positive contacts to allay the loneliness that Mr A sees as his main challenge.
This case study shows how carers can be abused by the adult they are caring for, and how to support them when this happens:
Mrs D lives with her husband, B. B has a long term brain injury which affects his mood, behaviour and his ability to manage close family relationships. This has often led to him shouting and hitting out at his wife, who is also his main informal carer. Mrs D told a professional who was involved in supporting her that she was becoming increasingly frightened by B's physical and verbal outbursts and at times feared for her personal safety.
Other family members were unaware of the extent of the harm and that Mrs D was exhausted and considering leaving the situation. The local authority became involved.
The situation presented significant personal risk to Mrs D but there was also a risk of fragmenting relationships if the local authority staff were not sensitive to the needs of the whole family. The practitioner, under supervision from her social work manager invested time in meeting with Mrs D to explore her preferences around managing her safety and how information about the situation would be communicated with the wider family and with B. This presented dilemmas around balancing the local authority's duty of care towards Mrs D with her wishes to remain in the situation with B. Placing emphasis on the latter inevitably meant that Mrs D would not be entirely free from the risk of harm but allowed the practitioner to explore help and support options which would enable Mrs D to manage and sustain her safety at a level which was acceptable to her.
The practitioner received regular supervision to allow time to reflect on the support being offered and to ensure that it was 'person centred'. The outcome for Mrs D was that she was able to continue to care for B by working in partnership with the local authority. The practitioner offered advice about how to safely access help in an emergency and helped her to develop strategies to manage her own safety – this included staff building rapport with B, building on his strengths and desire to participate in social activities outside the family home. The effect of this was that some of the trigger points of him being at home with his wife for sustained periods during the day were reduced because he was there less.
Mrs D also had a number of pre-existing support avenues, including counselling and a good relationship with her son and her friends. The situation will be reviewed regularly with Mrs D but for the time being she feels much more able to manage.
This case study demonstrates how agencies should work together to prevent abuse and neglect from occurring/reoccurring:
Miss P's mental health social worker became concerned when she had received reports that 2 of Miss P's associates were visiting more regularly and sometimes staying over at her flat. Miss P was being coerced into prostitution and reportedly being physically assaulted by one of the men visiting her flat. There was also concern that she was being financially exploited. Miss P's lack of understanding of how to protect herself when living alone was exacerbated by her mental health needs and consequent inability to set safe boundaries with the people she was associating with.
The social worker recognised that the most appropriate way to enable Miss P to manage the risk of harm was to involve Miss P's family, which she agreed to, and other professionals to develop and coordinate a plan which would enable her to continue living independently but provide a safety net for when the risk of harm became heightened. Guided initially by Miss P's wish for the 2 men to stay away from her, the social worker initiated a planning meeting between supportive family members and other professionals such as the police, domestic violence workers, support workers and housing officers. Although Miss P herself felt unable to attend the planning meeting, her social worker ensured that her views were included and helped guide the plan. The meeting allowed family and professionals to work in partnership, to openly share information about the risks and to plan what support Miss P needed to safely maintain her independence.
Tasks were divided between the police, family members and specialist support workers. The social worker had a role in ensuring that the plan was coordinated properly and that Miss P was fully aware of everyone's role. Miss P's family were crucial to the success of the plan as they had always supported her and were able to advocate for her needs.
They also had a trusting relationship with her and were able to notify the police and other professionals if they thought that the risk to Miss P was increasing. The police played an active role in monitoring and preventing criminal activity towards Miss P and ensured that they kept all of the other professionals and family up to date with what was happening. Miss P is working with a domestic violence specialist to help her develop personal strategies to keep safer and her support worker is helping her to build resilience through community support and activities.
These case studies shows how agencies can work together to provide a co-ordinated response during a criminal investigation:
Case study 1: Miss Y
Miss Y is a young woman with a learning disability with limited support from her family and was not engaged with health and social care services. Miss Y was befriended by an individual who took her to parties where she was given drugs and alcohol and forced to have sex with different men. Sometimes she would be given money or gifts in return for having sex with the men.
Miss Y disclosed this to a social worker and it was discovered that there were a number of young people and vulnerable adults who were being sexually exploited by multiple perpetrators. Miss Y lacked mental capacity in order to be able to consent to having sex, as well as in relation to her accommodation, finances or personal safety.
The perpetrators sought out Miss Y and others because of their perceived vulnerability – whether that was because of their isolated situation and social circumstances coupled with age, disability, mental illness, or their previous history as a victim of abuse. The process to safeguard Miss Y involved a coordinated response between the police, social care, health and voluntary and community sector organisations.
This included the police investigating the perpetrators for rape, sexual assault, trafficking and drug offences. The Court of Protection and Deprivation of Liberty Safeguards were also used initially to safeguard Miss Y.
Case Study 2: Mr P
Mr P has mild learning disabilities. The safeguarding concern was financial and other abuse and neglect by his brother, with whom he lived. His support worker had noticed that Mr P had begun to appear agitated and anxious, that he looked increasingly unkempt and that he was often without money; then he suddenly stopped attending his day centre.
When the support worker and the safeguarding officer followed up, Mr P told them that at times he was not allowed out at all by his brother and was confined to his bedroom. He was only allowed to use the bathroom when his brother said he could, and often didn't get enough to eat. He was also very worried because his bank card no longer worked, and he had no money, so couldn't buy food for himself.
Mr P consented to move to temporary accommodation, and a case conference was held, which he attended with an advocate. At his request a move to a supported living flat was arranged and his belongings were retrieved from his brother's property. His bank account had been emptied by his brother, so he has made new arrangements for his money.
The police are investigating both the financial abuse and the harm Mr P suffered at his brother's hands. He has begun to talk about his experiences and is gradually regaining his confidence.
This case study demonstrates how a Safeguarding Plan can be used to develop an adult's capacity to protect themselves from harm:
Mr A is 24 and has autism and a mild learning disability. He is a very friendly and sociable young man, who is prone to waving and talking to most people he comes across and who sees everyone as a potential friend. However, he struggles to read the intentions of others and is easily led astray and manipulated.
He lives next door to a pub, where he knows the staff and the regulars. He also lives close to his GP and is able to access his most frequently visited places. He does, however, like to walk into town to talk to people he meets out and about. On such occasions he has been repeatedly tricked into stealing items from a newsagent by a group of teenagers and given large amounts of money away to strangers he strikes up conversations with. Due to his previous experiences, Mr A was identified during a needs assessment as being at risk of abuse and neglect and a safeguarding enquiry was triggered.
The council found that, although Mr A was not currently experiencing abuse or neglect, he remained highly vulnerable to abuse due to his being well-known in his area as someone as easy to manipulate.
To assure his safety in the future, a safeguarding plan was agreed between Mr A and a social worker. This focused on developing his social skills and understanding of relationships and boundaries and the social worker worked with Mr A to consider various support options such as having a buddy or circle of support.
The social worker put Mr A in touch with an autism social group which provided sessions on skills for staying safe. As the group was based in town, Mr A's plan also included a support worker to accompany him. After the first 5 sessions Mr A was able to attend himself but continued to meet with his support worker on a monthly basis as part of the risk management strategy set out in his safeguarding plan.
Case Study 1: Mr R
Mr R, a 58-year-old man, has faced severe issues with hoarding that have compromised his safety and well-being. His small apartment is packed with items accumulated over years, creating unsafe living conditions. These behaviours stem from unresolved trauma and contribute to his worsening depression and anxiety, resulting in isolation and neglect of self-care.
Mr R’s mental capacity was assessed. He was unable to understand the risks associated with his environment, such as fire hazards and restricted emergency access and therefore lacked mental capacity in relation to this decision. A best interest decision was made to address the concerns with a social worker taking the lead in coordinating a comprehensive Care Act 2014 assessment and support plan.
The social worker's role involved building trust with Mr R, a key challenge due to his mistrust and resistance to intervention. Through consistent, empathetic communication, his anxiety around change reduced. The social worker collaborated with housing, mental health professionals and decluttering specialists to create a plan that respected Mr R’s autonomy while ensuring his safety.
Regular home visits took place with gradual decluttering sessions which were supervised to avoid overwhelming Mr R, and the professionals involved had regular multi-agency meetings to share information, update on progress and agree actions. The social worker also engaged community resources to foster a sense of connection, aiming to break the cycle of isolation. By overcoming these challenges with a patient, step-by-step approach, Mr R was supported to reclaim his living space and improve his quality of life.
Case Study 2: Mrs H
Mrs H was an older woman living alone, who was hoarding household items, including food and rubbish. Neighbours raised concerns due to the smell from her home. Mrs H had significant health problems, including malnutrition and untreated medical conditions. Her living conditions posed serious risks of falls and fire hazards.
Despite several attempts by social services to complete welfare checks, interventions were delayed. Tragically, Mrs H was later found deceased in her home, with the volume of hoarded items contributing to her inability to escape in an emergency.
This case highlights the need for timely and effective risk assessments. Collaboration between social services, healthcare providers, mental health professionals, and housing services are also key in addressing complex needs. Earlier involvement of mental health services could have supported Mrs H in managing her hoarding behaviour and health issues.
Effective communication, empathy and a non-judgemental approach may have helped to build trust with Mrs H. Involving family members and carers where available can provide additional support and help to understand the adult. Regular risk assessment reviews and close monitoring of the adult’s well-being are also essential.
Immediate action should be taken if safeguarding concerns arise. A proactive safeguarding approach could have prevented delays in Mrs H’s case.
Case Study 1: Ms E
Ms E, who lived alone, was at risk of severe complications due to malnutrition and dehydration. Her self-neglect was linked to untreated depression following the death of her partner. Ms E received visits from community nurses and mental health services, but they were initially working in isolation. Due to the high level of risk to Ms E, the duty to make enquiries under Section 42 of the Care Act was triggered.
A co-ordinated multi-agency approach was implemented, coordinated by the social worker assigned to Ms E’s case. The social worker conducted a thorough assessment of Ms E’s living conditions and health needs and tried to understand what and who were important to Ms E in relation to her care. The social worker coordinated regular multi-agency meetings with healthcare providers, mental health services, and community organisations sharing information and formulating actions plans which were communicated with Ms E. She advocated for Ms E’s needs, ensuring her voice was heard in the planning of her care, and identified and addressed risks to Ms E’s health and safety.
Ms E talked about being overwhelmed by having too many professional visits, so a lead professional was agreed, and visits were coordinated to suit Ms E. Ms E began to engage in accepting support and services at her pace, initially agreeing to take nutritional supplements and a small package of care. Eventually, Ms E accepted support for her depression.
Working within the framework of the Care Act 2014, the social worker promoted Ms E’s well-being and took a personalised approach. The effective multi-agency working and information sharing ensured that all relevant services were coordinated with a clear plan of support for Ms E.
Case Study 2: Mr M
Mr M, in his 70s, lives in an upper-floor council flat, and had hoarded over many years: his own possessions, items inherited from his family home, and materials he had collected from skips and building sites in case they came in useful. The material was piled from floor to ceiling in every room, and Mr M lived in a burrow tunnelled through the middle, with no lighting or heating, apart from a gas stove. Finally, after years of hiding in privacy, Mr M had realised that work being carried out on the building would lead to his living conditions being discovered. Mr M himself recounted how hard it had been for him to invite access to his home, how ashamed and scared he was, and how important his hoard was to him, having learnt as a child of the war never to waste anything.
Through working closely together, Mr M, his support worker and experienced contractors have been able gradually to remove from his flat a very large volume of hoarded material and bring improvements to his home environment. It has taken time and patience, courage and faith, and a strong relationship based on trust. The worker has not judged Mr M, and has worked at his pace, positively affirming his progress. Both Mr M and his support worker acknowledge his low self-esteem, and have connected with his doctor and mental health services. The worker has recognised the need to replace what Mr M is giving up, and has encouraged activities that reflect his interests. Mr M has valued the worker's honesty, kindness and sensitivity, his ability to listen and the respect and reciprocity within their relationship.
At the age of 72 years, Ms W, although registered disabled, was an active member in her community often seen helping at community events and visiting the local shops and swimming pool. Ms W had a fall in her home which left her lacking in confidence and fearful that she would fall again. As the winter approached, Ms W spent more time alone at home only venturing to the corner shop to buy groceries. As time passed her house came in disrepair and unhygienic as local youths began throw rubbish, including dog faeces into her front garden.
Within a 5 month period Ms W made 7 complaints to the police about anti-social behaviour in her local area, and on 2 occasions was the victim of criminal damage to the front of her house, where her wheelchair accessibility ramp has been painted by graffiti. The police made a referral to social services. As a result, Ms W was placed on a waiting list for a support service.
Four weeks after she was last seen Ms W committed suicide. A Safeguarding Adults Review (SAR) was convened according to the local policy that stated 'the purpose of an SAR is not to reinvestigate or to apportion blame, but to establish whether there are lessons to be learnt from the circumstances of the case about the way in which local professionals and agencies work together to safeguard vulnerable adults. The published report and recommendations which followed demonstrated the lessons from this case. The resultant action plan included:
- Strengthened relationships and information sharing between police officers, health and the local authority;
- Clear lines of reporting and joint working arrangements with the community safety partnerships;
- A robust multi-agency training plan;
- A targeted community programme to address anti-social behaviour;
- The development of a 'people's panel' as a sub group to the Safeguarding Adults Board which includes people who access services, carers and voluntary groups;
- The development of a 'stay safe' programme involving local shops where adults at risk of abuse may report their concerns to a trusted member if their community.
Further case studies can be found in the LGA/ADASS guidance: Understanding what constitutes a safeguarding concern and how to support effective outcomes.
This includes a case study based on the Howard case.
Last Updated: September 11, 2025
v44